Frozen Ropes – Mini Channels
Learn to identify low-volatility patterns and understand the risks when these predictable channels break
Some stock patterns are characterized by tight, low-volatility moves that seem obvious to all participants. These are known as mini channels, or “frozen ropes” as described by Dan Zanger. While rare, they represent crucial moments in a stock’s life cycle. When these patterns break, they often lead to sharp, rapid profit-taking or even full trend reversals.
This lesson focuses on identifying frozen ropes, understanding their implications, and knowing how to act when they break.
Learning Objectives
By the end of this lesson, you will be able to:
- Identify mini channels or frozen ropes on stock charts
- Understand the risks associated with frozen ropes breaking
- Develop strategies for managing positions during and after a frozen rope formation
What Are Mini Channels or Frozen Ropes?
A frozen rope is a multi-week, low-volatility price pattern that progresses in a tight, predictable channel. This pattern becomes highly noticeable to market participants because of its consistency and lack of significant price swings.
- Key Characteristics:
- Low Volatility: The stock moves steadily in one direction with minimal fluctuations
- Tight Range: Price action is confined to a narrow channel, often aligning closely with a short-term moving average like the 5-day EMA
- Predictable Behavior: The pattern’s uniformity makes it “obvious” to traders
Why Are Frozen Ropes Important?
Frozen ropes often signal a stock that has attracted heavy accumulation or speculative interest. However, their breakdown can result in sharp, rapid profit-taking, as the lack of volatility creates pent-up selling pressure.
- Typical Outcomes When They Break:
- Quick declines, often with a significant gap down
- Sharp intraday drops of 10% or more, as seen in examples like AMBA
- Potential for the entire trend to unwind
Managing Positions in Frozen Ropes
Recognizing Frozen Ropes
To identify a frozen rope:
- Look for a tight, low-volatility channel lasting several weeks
- Observe if the stock begins to “ride” short-term moving averages like the 5-day EMA
Act Quickly When They Break
When a frozen rope breaks, action must be decisive:
- Pre-Market or Open: Be prepared to sell immediately when the break is confirmed
- Gap-Downs: Often, these breaks occur with a gap down, signaling a sudden shift in sentiment
Signs of an Imminent Break
- Look for subtle signs like a sudden lack of volume support, reversal candles, or unusual gaps in the opposite direction of the trend
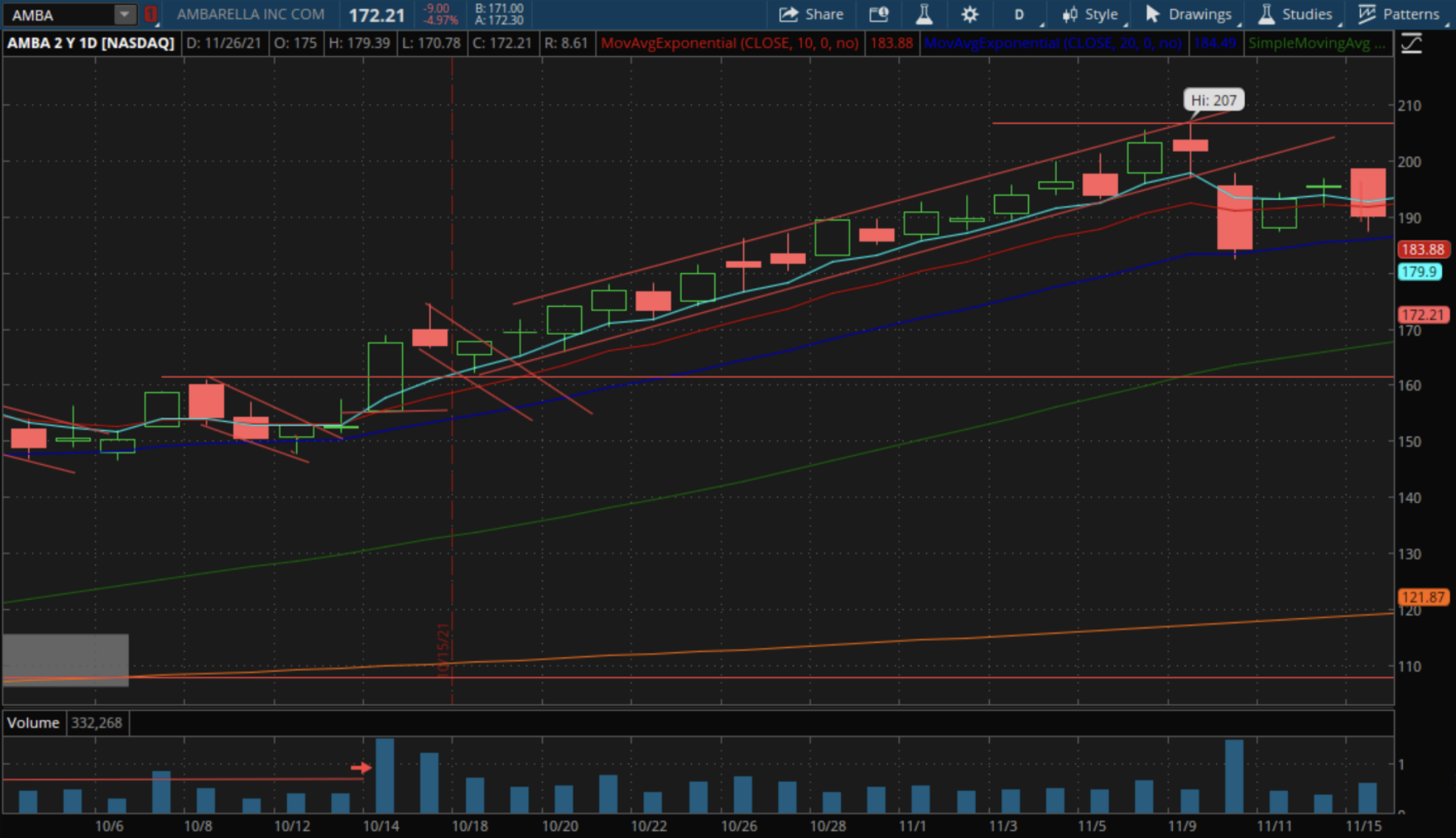
Example: AMBA Frozen Rope
- AMBA formed a well-defined frozen rope over several weeks, tightly confined to an upward channel
- Upon breaking, the stock dropped 10% in a single day, highlighting the need for swift action
Limitations and Rarity of Frozen Ropes
While useful, frozen ropes are not common. Their rarity means they shouldn’t be a central focus of your trading strategy but rather a tool in your broader trading arsenal.
Reflection
Recall a trade where you gave back profits after a stock became overextended. How could selling into strength have improved your results?
Conclusion
Selling into strength by managing extensions is a proactive way to lock in gains and reduce exposure to potential reversals. While no strategy is perfect, combining extension analysis with moving averages, trendlines, and broader market context gives you the tools to maximize profits while minimizing risk.
Remember, it’s not just about protecting your position but optimizing your outcomes. As you refine your approach, extensions will become an integral part of your trading toolkit.
Action Items
- Review your current positions and identify any stocks approaching significant extension levels
- Define thresholds for selling into strength based on stock personality and market conditions
- Practice tracking extensions in a trading journal to refine your judgment over time
